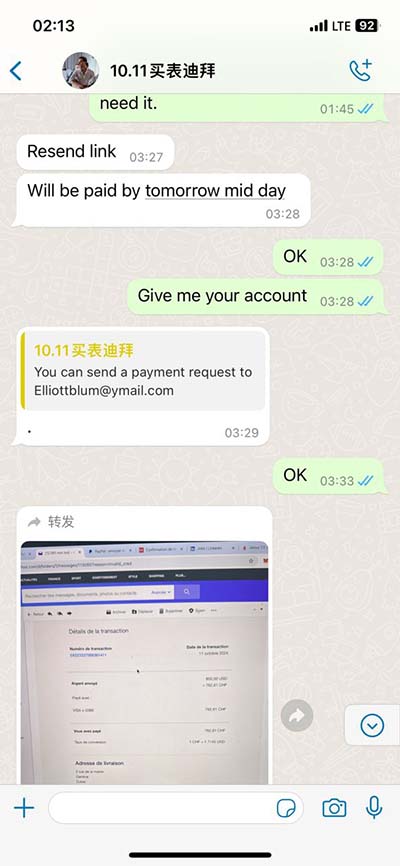
so is this from watching media fake news | Why do people around the world share fake news? New research so is this from watching media fake news Many Americans share fake news on social media because they’re simply not paying attention to whether the content is accurate — not necessarily because they can’t tell real from made-up news, a new study in Nature suggests. 1 talking about this
0 · Why do people around the world share fake news? New research
1 · What can be done to reduce the spread of fake news? MIT Sloan
2 · To foil fake news, focus on infectiousness
3 · The real 'fake news': how to spot misinformation and disinformation
4 · How to spot 'fake news' online
5 · Fake news: What it is, and how to spot it
6 · Fake news: What is it? And how to spot it
7 · Fact
8 · A main reason people share fake news: Lack of attention, study
9 · A fake news survival guide: How to identify misinformation
Earthbound Immortal Ccapac Apu X DARK Level 10 [ Fiend / Effect ] ATK 3000 DEF 2500 There can only be 1 "Earthbound Immortal" monster on the field. If there is no face-up Field Spell on the field, destroy this card.During your Main Phase: You can add 1 "Earthbound Immortal" monster from your Deck or GY to your hand. If an "Earthbound Immortal" monster is Normal Summoned while this monster is on the field: You can make your opponent's LP 3000. You can only use each effect of "Earthbound Greater Linewalker" once per turn.
So you think a story or photo you've seen online might be fake - or exaggerated. Here's what you need to know about fake news online. First tip - stop calling it fake news.
Many Americans share fake news on social media because they’re simply not paying attention to whether the content is accurate — not necessarily because they can’t tell real from made-up news, a new study in Nature suggests. The research team’s findings have implications for how social media companies can stem the flow of misinformation. Platforms could, for instance, implement simple accuracy prompts to shift users’ attention towards the reliability . In this episode, Zhang will give you tips you can use — and share with your friends and family — on how to tell if a story you come across on social media is real or fake. Fake news continues to proliferate - but how much do you know about separating fact from opinion, or truth from hoax? Online misinformation is slippery to define - but it has huge implications for everything from politics to health.
Fake news is news or stories on the internet that are not true. There are two kinds of fake news:
BBC Monitoring’s disinformation specialist Shayan Sardarizadeh shares his top tips on spotting 'fake news' including: Check your source; Look closer at the footage or image; Is there anything. Since the 2016 U.S. Presidential election and British “Brexit” referendum — and then COVID-19 — opened the floodgates on fake news, research has delved into the psychology behind online misinformation
louis vuitton supreme case iphone 7 plus
Why do people around the world share fake news? New research
The best way to counter fake news is to limit person-to-person spread, Stanford study finds. New research on the ways fake news spreads via social media refines conventional wisdom and offers potential solutions to a vexing problem. While the Covid-19 pandemic has seen a surge in misinformation about the virus and vaccines, YouTube and other social media platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp and Twitter have been plagued with. So you think a story or photo you've seen online might be fake - or exaggerated. Here's what you need to know about fake news online. First tip - stop calling it fake news. Many Americans share fake news on social media because they’re simply not paying attention to whether the content is accurate — not necessarily because they can’t tell real from made-up news, a new study in Nature suggests.
The research team’s findings have implications for how social media companies can stem the flow of misinformation. Platforms could, for instance, implement simple accuracy prompts to shift users’ attention towards the reliability . In this episode, Zhang will give you tips you can use — and share with your friends and family — on how to tell if a story you come across on social media is real or fake.
Fake news continues to proliferate - but how much do you know about separating fact from opinion, or truth from hoax? Online misinformation is slippery to define - but it has huge implications for everything from politics to health. Fake news is news or stories on the internet that are not true. There are two kinds of fake news:
BBC Monitoring’s disinformation specialist Shayan Sardarizadeh shares his top tips on spotting 'fake news' including: Check your source; Look closer at the footage or image; Is there anything. Since the 2016 U.S. Presidential election and British “Brexit” referendum — and then COVID-19 — opened the floodgates on fake news, research has delved into the psychology behind online misinformation
The best way to counter fake news is to limit person-to-person spread, Stanford study finds. New research on the ways fake news spreads via social media refines conventional wisdom and offers potential solutions to a vexing problem. While the Covid-19 pandemic has seen a surge in misinformation about the virus and vaccines, YouTube and other social media platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp and Twitter have been plagued with. So you think a story or photo you've seen online might be fake - or exaggerated. Here's what you need to know about fake news online. First tip - stop calling it fake news.
Many Americans share fake news on social media because they’re simply not paying attention to whether the content is accurate — not necessarily because they can’t tell real from made-up news, a new study in Nature suggests. The research team’s findings have implications for how social media companies can stem the flow of misinformation. Platforms could, for instance, implement simple accuracy prompts to shift users’ attention towards the reliability . In this episode, Zhang will give you tips you can use — and share with your friends and family — on how to tell if a story you come across on social media is real or fake. Fake news continues to proliferate - but how much do you know about separating fact from opinion, or truth from hoax? Online misinformation is slippery to define - but it has huge implications for everything from politics to health.
Fake news is news or stories on the internet that are not true. There are two kinds of fake news: BBC Monitoring’s disinformation specialist Shayan Sardarizadeh shares his top tips on spotting 'fake news' including: Check your source; Look closer at the footage or image; Is there anything. Since the 2016 U.S. Presidential election and British “Brexit” referendum — and then COVID-19 — opened the floodgates on fake news, research has delved into the psychology behind online misinformation
The best way to counter fake news is to limit person-to-person spread, Stanford study finds. New research on the ways fake news spreads via social media refines conventional wisdom and offers potential solutions to a vexing problem.
louis vuitton stijgt in waarde

What can be done to reduce the spread of fake news? MIT Sloan
louis vuitton stiefel damen
To foil fake news, focus on infectiousness
Manzo, the intimate, 70-seat restaurant that completes the sometimes raucous Eataly complex anchoring the reimagined Park MGM on the Strip, is at least outwardly a stunning contrast to its.
so is this from watching media fake news|Why do people around the world share fake news? New research